isolation of organic compounds through pasteur pipette|chemical extractions procedures pdf : companies All techniques for isolation and purification of products use phase equilibria: isolate the desired product into one phase that is in equilibrium with another phase. The second phase ideally . Count on us for an unrivaled selection of lab, life sciences, safety, and facility management supplies—including chemicals, equipment, instruments, diagnostics, and much more—along .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Priorclave can find the right laboratory autoclave for your team, with options ranging from small chamber volume benchtop autoclaves to larger pass-through autoclaves.
Extraction #1. As CH2Cl2 CH 2 Cl 2 is prone to emulsions, invert the funnel and shake gently for one minute with venting. After allowing the layers to separate in the funnel, drain the bottom organic layer into a clean Erlenmeyer flask (and label the flask, e.g. "bottom organic layer").Allow the layers to separate and carefully draw off the bottom layer with Pasteur pipette, depositing it in a second (properly labeled) centrifuge tube. Repeat the procedure with two .All techniques for isolation and purification of products use phase equilibria: isolate the desired product into one phase that is in equilibrium with another phase. The second phase ideally .4. Add the silica to the solvent, a little at a time, while swirling. Use a Pasteur pipette or glass rod to mix the slurry. 5. Pour or pipette some of the slurry into the column. Allow the solvent to drain to prevent overflowing (Fig. 3, step C). 6. Tap the column gently to encourage bubbles to rise and the silica to settle (Fig. 3, step D). 7.
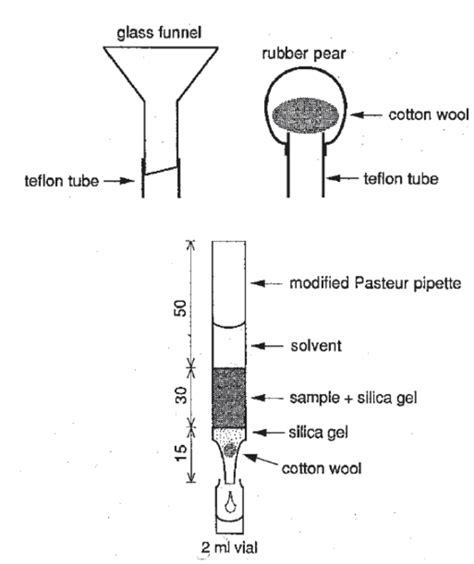
The Pasteur pipette is an essential tool in many scientific disciplines, including biology, chemistry, and medicine. The Pasteur pipette consists of a straight glass tube with a rounded or tapered end. The narrow end is used to draw up or dispense liquids. The pipette is usually made of borosilicate glass, which is resistant to heat and chemicals. Isolation is accomplished by filtering out the insoluble contaminants and recovering the target compound from the filtrate (solution that passes through filter). This method generally requires a single extraction, and an outline of the general procedure is below.Using a Pasteur pipette, water was added to the flask dropwise. In addition to a boiling stick, the solution was heated on a hot plate. Once boiling began, water was added until the solid dissolved. The flask was set on a cork ring (or any other insulator) and allowed to cool to room temperature once the boiling stick was removed.Organic Chemistry: Techniques and Transformations 1 LABORATORY 3 . Using a Pasteur pipette, add 0.5-1 mL of the boiling solvent to the flask containing the benzoic acid. Swirl the flask with each addition and place it on the hot plate to keep it a . air through the filter cake for a few minutes to promote drying. Transfer the crystals to a
Using Pasteur Pipettes. Pasteur pipettes (or pipets) are the most commonly used tool for transferring small volumes of liquids (< \(5 \: \text{mL}\)) from one container to another. They are considered disposable, although some institutions may clean and reuse them if they have a method for preventing the fragile tips from breaking. Preparative chromatography is one of the most common and important purification techniques in organic chemistry and is employed in laboratories across the globe. In order to facilitate student proficiency with the method, a unique approach for the separation of estragole, ethyl cinnamate, and cinnamyl alcohol using microscale preparative flash column . Cerritos Community College Organic Chemistry 211 Laboratory Extraction (Part 2) Separation of Acidic, Basic, and Neutral Components Introduction: Most neutrally charged organic compounds are highly soluble in organic solvents and fairly insoluble in polar solvents. Acid-base extractions are a type of extraction that takes advantage of changes in solubility due to acid .liquid with a Pasteur pipette to a small test tube. Column Chromatography 1. Prepare a silica gel column using a Pasteur pipette as follows: a. Insert a small ball of cotton into the top of the column and carefully push it down onto the neck of the pipette. b. Add about 2.0 cm of silica gel to the pipet and tap the column with your finger to pack
pasteur pipette extraction procedure
Organic Chemistry 3rd Edition . Analytical Chemistry Finals Vocab Review. 84 terms. joshua5916. Preview. gci ch 2 to ch 4. 33 terms. yukinow13. . We said that if you use a Pasteur pipette with a small plug of cotton in the neck, you can use the air to remove volatile solvents. What color tab is on the air valve?
Cerritos Community College Organic Chemistry 211 Laboratory Isolation and Characterization of a Natural Product: Caffeine. O O CH3 N H HN – H3C N O N N O N N P OH H2N N O O N N N N O H3C OH purine 2'-deoxyguanosine caffeine 5'-phosphate In this experiment, the techniques of solid-liquid extraction and liquid-liquid extraction will be used to isolate caffeine from tealeaves.Chemistry 2273a - 2009 3 Figure 2: Illustration of a column chromatography separation of a mixture of 3 components, A, B and C. Compound A is the least polar and compound C is the most polar and the separation occurs as solvent is allowed to flow through the stationary phase.
How to obtain a pure compound from a crude mixture: 5 Key Purification Techniques. Previously, we showed a few examples of preparing crude extracts from plants and other organisms. While sometimes (rarely) we get lucky and obtain an extract that is predominantly one compound, a more representative situation is that a mixture of compounds . With the aid of a Pasteur pipette If you want to remove the supernatant liquid from a solid in a vessel (vial, Erlenmeyer, etc.) you can use a Pasteur pipette. The pipette, provided with a teat, is introduced to the bottom of the container, so that it is completely stuck to the container, and it is sucked so that the solid will remain at the .Organic compounds synthesized in the laboratory or isolated from natural sources are . Using a Pasteur pipette, add 0.5-1 mL of the boiling solvent to the flask containing the benzoic acid. Swirl . and pull air through the filter cake for a few minutes to promoteChemistry Organic Chemistry Laboratory Experiments 2011-07-14 Extraction of Caffeine from Energy Drinks . SPE is a technique that allows the isolation of organic components dissolved in an aqueous mixture. In this procedure, the mixture is passed through a solid nonpolar matrix . Pasteur pipets Capillary tubes TLC plates Cotton
chemical extractions procedures pdf
Experiment 6: Isolation of Naproxen Cal Poly Pomona CHM 2010L 9. Add a small amount of anhydrous sodium sulfate for final drying. If there is still suspended particulate matter, you can do a crude filtration by inserting a small plug of cotton in a Pasteur pipette and pipetting the organic phase through that plug into a small, clean, dry pre-weighed round bottom flask or .
2. In TLC and column chromatography, separation occurs because of interactions between the organic compounds and the stationary phase 3. TLC can be used to monitor a reaction or quickly check for the purity of a mixture 5. in TLC and column chromatography, the mobile phase is called the eluent 6. In TLC, the most polar compounds go up the TLC plate the slowest, while in . A Pasteur pipette is convenient for adding the sample to the column. . passes through the compound adsorbed on the column or on the plate, it competes with silica for that compound. How successful the competition is depends on the strength of interactions between the solvent and the compound, versus the strength of interactions between the .
yellow pipette tips price
I have a novel compound that is insoluble in water. I have tried cyclodextrines and varying pHs. I have also tried to presolubilize in a wide variety of solvents (hexane, ACN, alcohols, DMSO .The recent isolation of the first representative of the termite group 1 phylum (now Elusimicrobia) was enabled by selecting for ultramicrobacteria through filtration of beetles gut homogenate through 0.2-μm-pore-size membrane filters but employing anoxic cultivation media with standard concentrations (i.e., 2 mM) of organic carbon substrates .
This experiment demonstrates the process of recrystallization of benzoic acid from water for the purpose of purifying an organic compound. The yield of the recrystallization process can. 124 ̊C for the final product in this experiment. A range of 3 ̊C is somewhat broader than would be expected for a pure compound.Pipette Pasteur extraction: a fast, convenient, . Furthermore, mixing organic compounds with minerals using either high energy appartus, e.g. ultrasonic (Lichtfouse et al., 1997), . samples with a flow-through extraction cell. Analytical Chemistry 50, 663-665. Sieskind O. and Albrecht P. (1985) Efficient synthesis of rearranged cholest-13 . d. Isolation of a neutral species Most neutral compounds cannot be converted into salts without changing their chemical nature. Many of these neutral compounds tend to react in undesired ways i.e., esters undergo hydrolysis upon contact with strong bases or strong acids. One has to keep this in mind as well when other compounds are removed.
For sample application, better use a short Pasteur pipette since long ones easily brake and fall onto the gel material. 24. Any compounds that stick to the Sephadex LH-20 or Toyopearl HW-40 gel material can be eluted with a 9 + 1 mixture of methanol and 1 M ammonium acetate (alternatively, 1% acetic acid in methanol can be used).Figure 1.89: Creating and using a filter pipette: a) Piece of cotton, b+c) Shoving cotton to the bottom of the pipette, d) Filtering a mixture into a GC vial, e) GC vial held with an upside down large septum. To create a pipette filter, use a long rod to wedge a small piece of cotton into the bottom of a Pasteur pipette (Figure 1.89a-c).14.) Being careful not to disturb the solid at the bottom of the tube, transfer the supernatant liquid with a pasteur pipette to a test tube or small beaker. Column Chromatography. 1.) Prepare an alumina column using a pasteur pipette and a small cotton ball into the top of the column. 2.) Add about 0 g of alumina and finger tab the pasteur pipette
sterilizers (also known as autoclaves), many staff do not know the differences between the major types. Sterilisation using saturated steam kills microorganisms by transferring heat onto the .
isolation of organic compounds through pasteur pipette|chemical extractions procedures pdf